Spectrum of Manifestations and Therapeutic Outcomes in Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada Syndrome
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v41i4.2112
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v41i4.2112Abstract
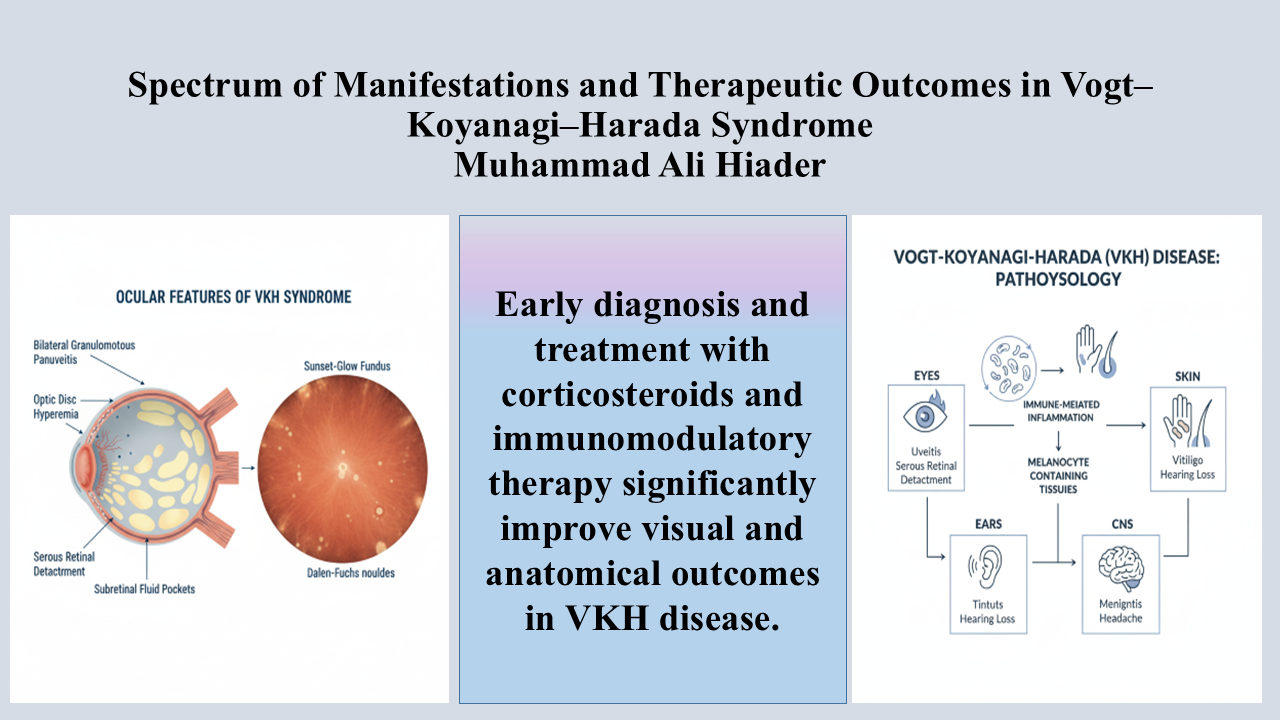
Purpose: To evaluate the clinical manifestations, management strategies, and treatment outcomes of Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada (VKH) disease in a tertiary care facility of Punjab.
Study Design: Retrospective chart review.
Place and Duration of Study: Al-Ehsan welfare eye Hospitalfrom January 2023 to December 2023.
Methods: There were 26 patients who qualified the inclusion criteria. VKH was diagnosed based on internationally updated diagnostic criteria. They underwent high dose steroids and immunomodulatory therapy. Demographic information, clinical presentations, treatment approaches, and results, such as CMT (central macular thickness) and BCVA (best-corrected visual acuity), were collected. SPSS version 22 was used for the statistical analysis, and a p-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: The mean age of patientswas 35.09 ± 8.8 years, with a predominance of females (61.5%). Treatment involved high-dose corticosteroids and immunomodulatory therapy. BCVA improved from 1.1 ± 0.86 logMAR at baseline to 0.61 ± 0.138 logMAR after 6 months (p < 0.01). Macular thickness decreased from 596 ± 247µm to 236.9 ± 27.1µm after 6 months (p < 0.01). There was a positive correlation of premature treatment termination and relapse (r = 0.490, p = 0.013).
Conclusion: Early diagnosis and treatment with corticosteroids and immunomodulatory therapy significantly improve visual and anatomical outcomes in VKH disease. The findings highlight the necessity of timely diagnosis, adherence to treatment, and a multidisciplinary approach to optimizepatient management and minimize complications.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr Muhammad Ali Haider; Uzma Sattar, Muhammad Amjad

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






