Balance Training Exercises and Mobility in Children with Visual Impairments: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v41i2.2004
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v41i2.2004Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effects of Balance Training Exercises on mobility in open and closed environments in children with Visual Impairments.
Study Design: A Randomized controlled trial.
Place and Duration: Rising Sun Special School from December 2022 to May 2023.
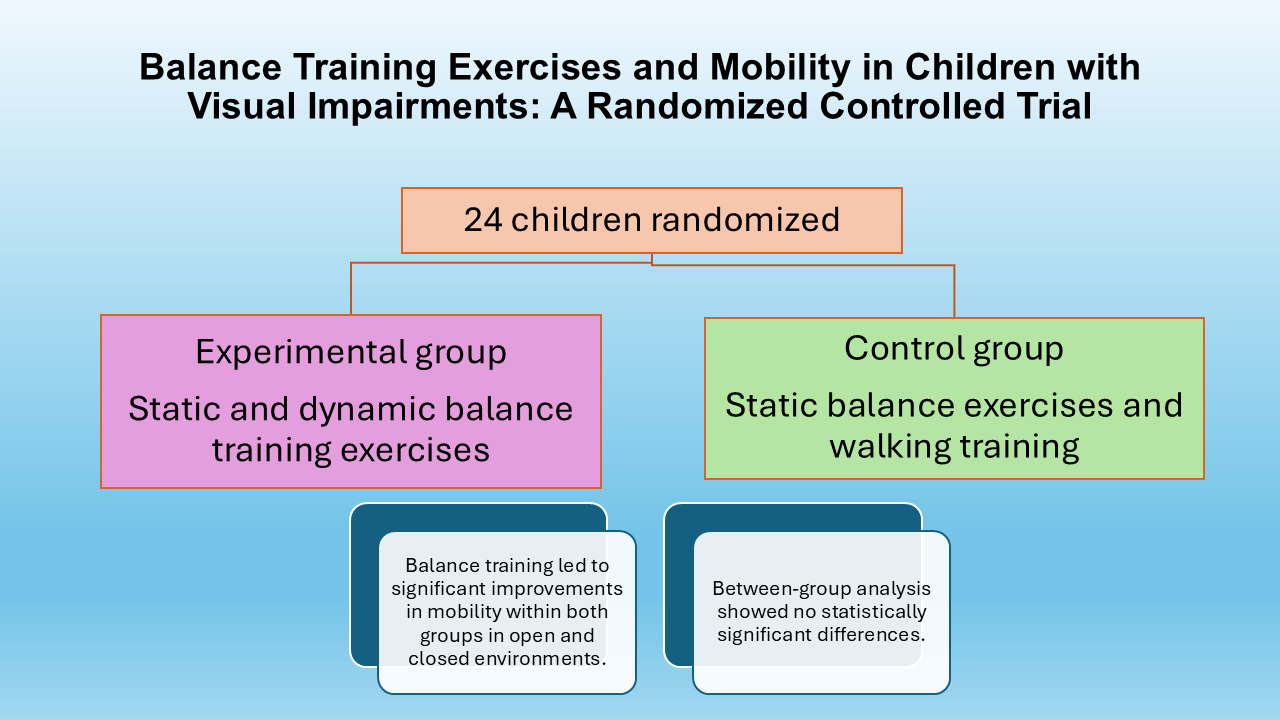
Methods: A total of 24 children with visual impairments were randomly assigned to experimental and control groups. Pretest assessments using the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test and the Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM-88) were conducted after an initial instructional session. The experimental group received both static and dynamic balance training exercises, while the control group received static balance exercises and walking training twice a week for eight weeks. Post test assessments were conducted after 16 training sessions.
Results: Significant improvements were observed in GMFM-88 scores for both the experimental and control groups in open and closed environments (p = 0.002 and 0.003, respectively). Similarly, TUG scores showed significant improvement (p = 0.000 and 0.001, respectively).The Mann-Whitney test showed no statistically significant difference between groups for GMFM-88 in open and closed environments (p = 0.154). Similarly, no significant difference was found for TUG scores (p = 0.154).
Conclusion: Balance training led to significant improvements in mobility within both groups in open and closed environments. However, between-group analysis showed no statistically significant differences. Despite this, clinical improvements in mobility were observed.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mubashra Tariq, Fareeha Kausar, Maria Khalid, Dr Wajida, Sana Umar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






