Effectiveness of Temporary Keratoprosthesis in Vitreo-Retinal Surgeries
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v41i2.1929
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v41i2.1929Abstract
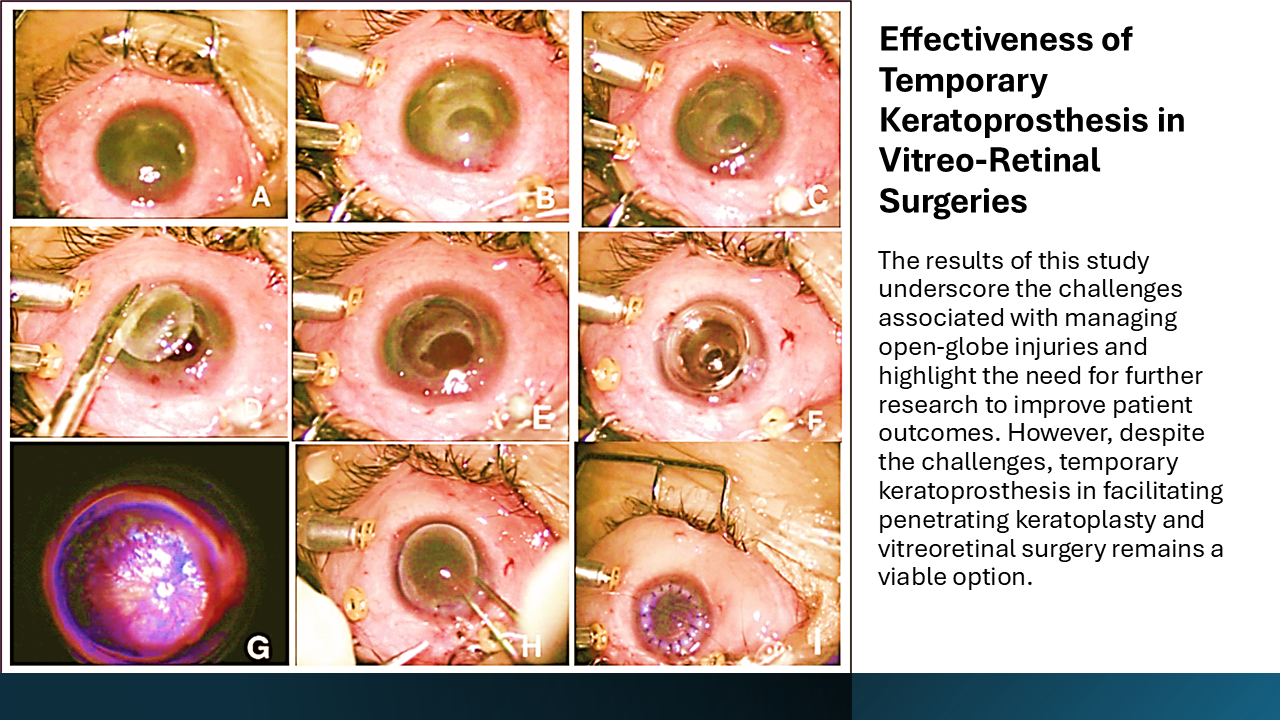
Purpose: To determine the effectiveness of temporary keratoprosthesis in facilitating successful combined penetrating Keratoplasty and vitreoretinal surgery.
Study Design: Retrospective interventional case series.
Place and Duration of Surgery: Department of Ophthalmology, Peshawar Medical College, from January 2020 and December 2023.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted which included 15 patients who underwent combined penetrating Keratoplasty and temporary keratoprosthesis-assisted vitreoretinal surgery. Data for pre and postoperative visual acuity, IOP, retinal attachment and graft status were obtained from hospital records. Surgical success was determined by the presence of a clear corneal graft, stable retinal attachment, normal intraocular pressure, and maintained or improved visual acuity. Data was analyzed using SPPS version 24. An independent test was employed to compare continuous variables between patients with successful and unsuccessful surgical outcomes.
Results: A total of 15 cases with mean age of 39.27 ± 15.88 years were included in this study. Visual acuity improved in 33.3% of cases, worsened in 13.3%, and remained stable in 53.3%. Postoperative corneal opacity occurred in 73.3% of patients, while 26.7% retained a clear graft. Functional vision was achieved in approximately 40% of the cases while only 13.3% were considered surgical success.
Conclusion: Complete surgical success was attained in only a minority of cases, and functional vision was achieved in less than half of the patients. Graft failure was the predominant postoperative complication, while corneal laceration with posterior segment pathology was the most frequent surgical indication.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammzad Zaheer Ullah Babar, Faisal Nawaz, Abdul Munim, Asif Ali, Muhammad Usman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






