Primary Internal Limiting Membrane Peel and Its Effects on Epiretinal Membrane After Pars Plana Vitrectomy for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v40i3.1792
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v40i3.1792Abstract
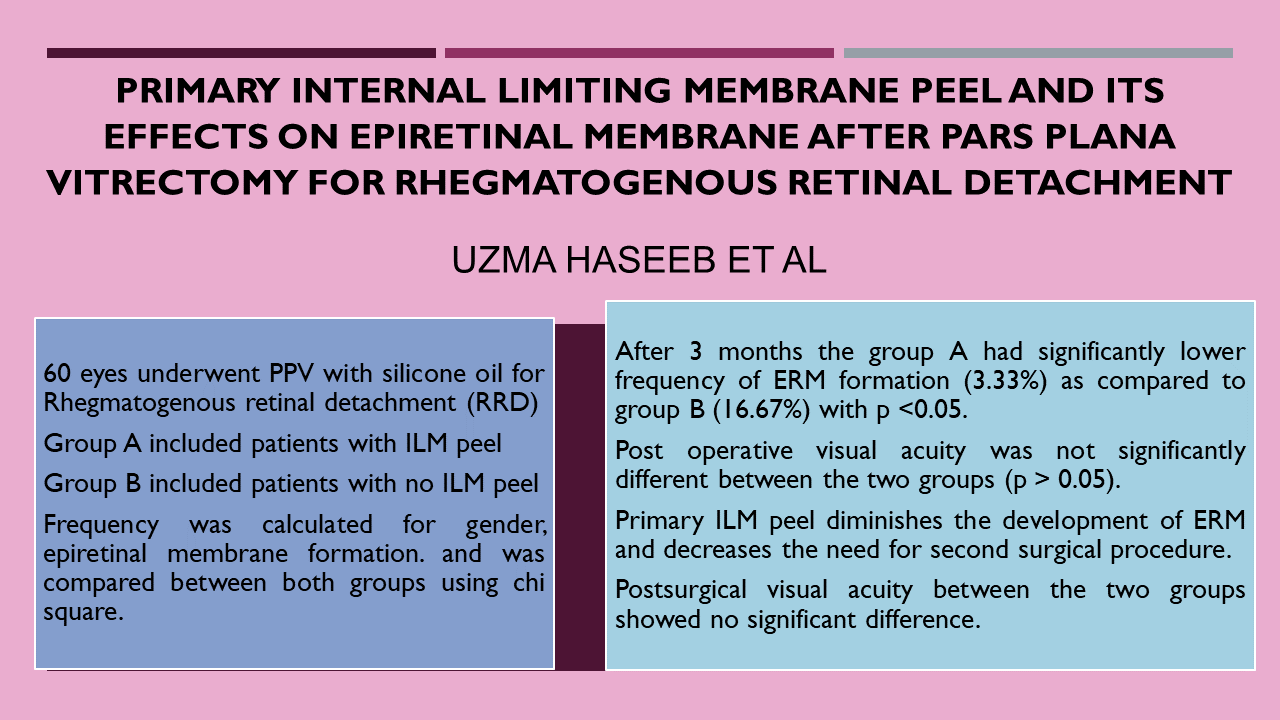
Purpose: To determine the effect of internal limiting membrane (ILM) peel in post-operative development of epiretinal membrane and to see visual outcomes of patients undergoing pars plana vitrectomy with and without ILM peel.
Study Design: Quasi experimental study.
Place and Duration of Study: Retina clinic of Al-Ibrahim Eye Hospital from July, 2022 to Dec, 2022.
Methods: A total of 60 eyes which underwent pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with silicone oil for Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) were included. Patients with previous vitreoretinal surgery or ocular trauma, macular diseases or coexisting conditions that could affect the outcomes or complicate the surgery were excluded. Group A included patients with ILM peel and Group B included patients with no ILM peel (30 eyes each). Frequency was calculated for gender, epiretinal membrane formation. and was compared between both groups using chi square.
Results: Mean age in group A was 47.63 ± 8.61 years and in group B was 45.36 ± 6.63 years. Gender distribution showed 66.6% males in group A and 43.3% in group B. After 3 months the group A had significantly lower frequency of ERM formation (3.33%) as compared to group B (16.67%) with p <0.05. However, post operativevisual acuity was not significantly different between the two groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: This study shows that primary ILM peel diminishes the development of ERM and decreases the need for second surgical procedure. However, postsurgical visual acuity between the two groups showed no significant difference.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Uzma Haseeb, Muhammad Haseeb, Tauseef Mahmood

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






