Coexistence of Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Foot in Patients Admitted at Indoor Facility of a Tertiary Care Center
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v40i2.1782
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v40i2.1782Abstract
Purpose: To determine frequency of “diabetic retinopathy (DR)” in patients admitted at a tertiary care hospital with diabetic foot.
Study Design: Cross sectional study.
Place and Duration of Study: HBS medical and dental college, Islamabad from November 2022 to November 2023.
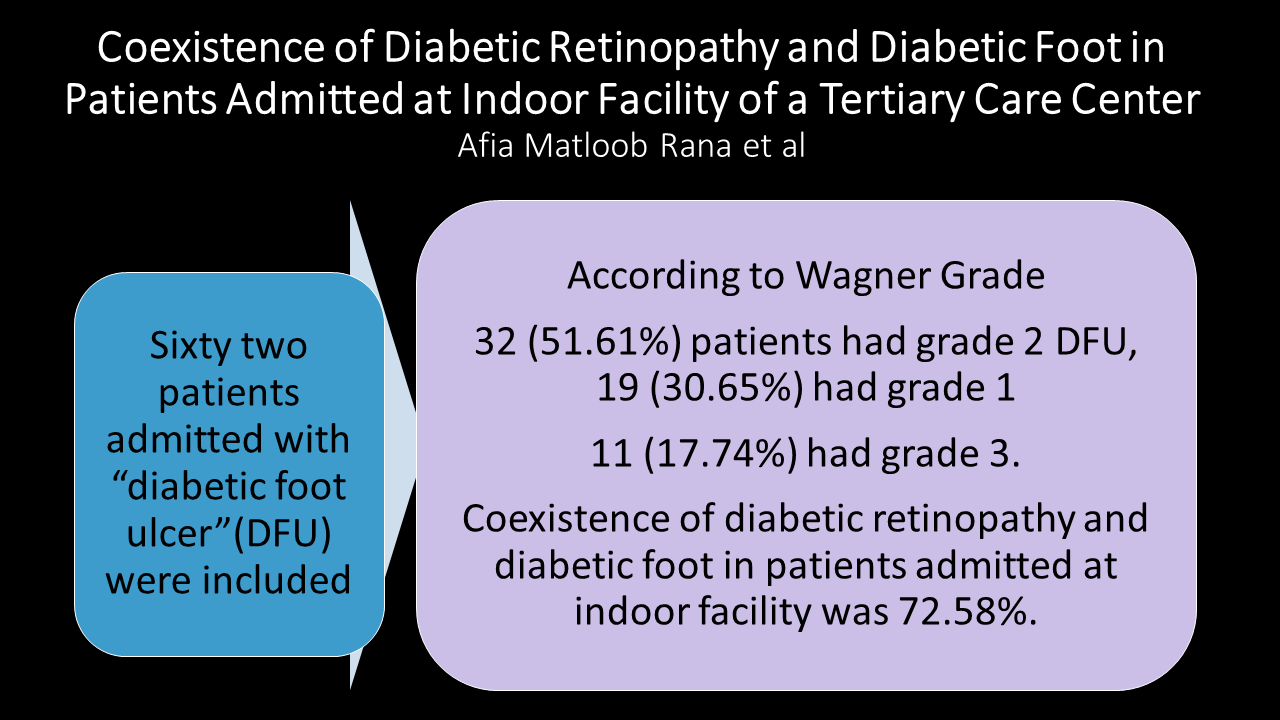
Methods: Sixty two patients admitted with “diabetic foot ulcer”(DFU) were included in this study. Severity of DFU was assessed using . Patients were assessed for presence of “diabetic retinopathy (DR)” as well as its severity. Data was analyzed using SPSS 22.
Results: Mean age was 49.37 ± 11.02 years. There were 34 (54.84%) males and 28 (45.16%) females. Mean HbA1C% was 9.46 ± 1.11%. Mean duration of diabetes was 10.06 ± 5.53 years. Forty five percent patients had diabetic retinopathy (DR). Amongst these patients diagnosed with DR (n = 45), 6 (13.33%) had mild non-proliferative DR, 20 (44.44%) had moderate non-proliferative DR, 14 (31.11%) had severe non-proliferative DR and 5 (11.11%) had proliferative DR. According to Wagner Grade there were 32 (51.61%), patients with grade 2 DFU, 19 (30.65%) had grade 1 and 11 (17.74%) had grade 3. Coexistence of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic foot in patients admitted at indoor facility was 72.58%.
Conclusion: Prevalence of “diabetic retinopathy (DR)” in patients admitted with diabetic foot was 72.58%. Presence of diabetic foot can be considered as strong predictor of presence of concomitant “diabetic retinopathy”.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Afia Matloob Rana, Erum Yousafzai, Humara Gul, Waseem Akhter

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






