Immediate Effect of Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection on Intraocular Pressure
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v40i2.1710
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v40i2.1710Abstract
Purpose: Raised intra ocular pressure following intravitreal Bevacizumabis a potential side effect which can be clinically significant. The aim of the study was to evaluate short term changes in intraocular pressure after intravitreal Bevacizumab injection.
Study Design: Quasi experimental study.
Place and Duration of Study: Benazir Bhutto Hospital, Rawalpindi from January 2021 to July 2021.
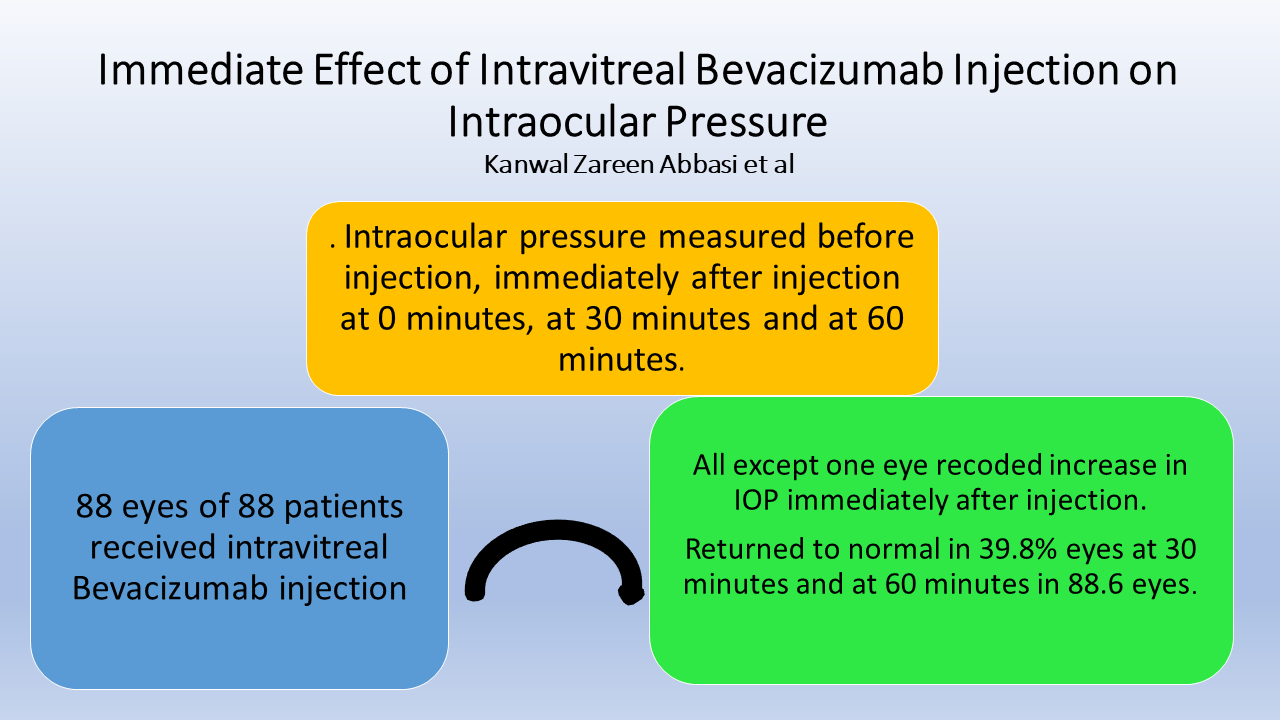
Methods: This study includes 88 eyes of 88 patients who received intravitreal Bevacizumab injection. Both females and males between the ages of 10 and 80 years, with any indication for intravitreal Bevacizumab, were included. Intraocular pressure (IOP) was measured before injection, immediately after injection at 0 minutes, at 30 minutes and at 60 minutes. Paired t test was used to compare post injection changes in IOP from baseline.
Results: All except one eye recoded increase in IOP immediately after injection. It returned to normal range in35 (39.8%) eyes at 30 minutes and at 60 minutes 78 (88.6%) eyes had normal IOP. Highest mean IOP was recorded immediately after injection which was 30.89+5.648and that reduced to 23.08+4.516 at 30 minutes and 18.14+2.623 at 60 minutes. Paired t test showed that the changes were significantly higher from baseline 13.30+2.78 at these intervals after injection.
Conclusion: An increase in intraocular pressure after intravitreal Bevacizumab injection is a frequent occurrence; however, for the majority of patients, it is transient and returns to normal levels within one hour.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Dr Kanwal ZareenAbbasi, Dr Ameera Jameel, Dr Wajeeha Rasool, Dr Bilal Humayun Mirza, Dr Sajid Rafiq Abbasi, Dr Misbah Munshi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






