Effects of Intra-cameral Dexamethasone after Uncomplicated Phacoemulsification
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v39i4.1581
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v39i4.1581Keywords:
Phacoemulsification, Dexamethasone, Flare, Cells.Abstract
Purpose: Postoperative inflammation is very common following phacoemulsification. We conducted this study to compare the effectiveness of intra-cameral dexamethasone injection with traditional topical steroids following phacoemulsification.
Study Design: Quasi experimental
Place and Duration of Study: Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Center, JPMC, Karachi from February 2022 to July 2022.
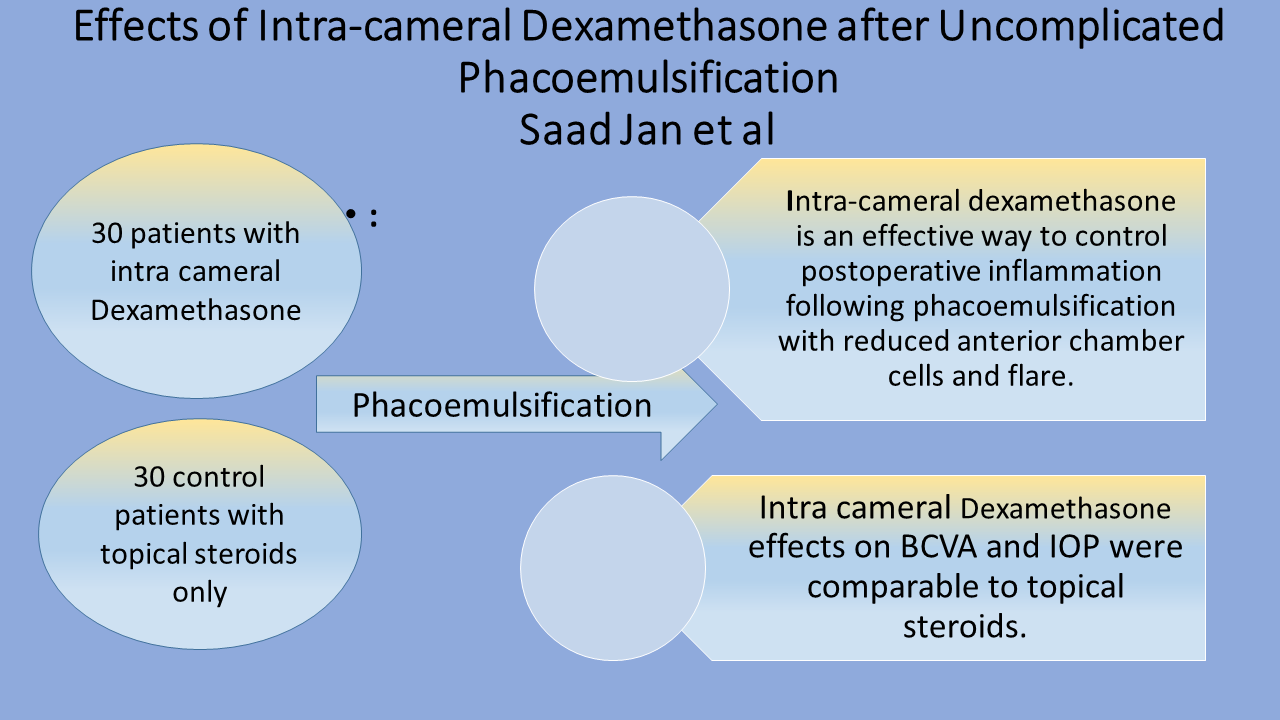
Methods: A total of 60 patients were divided into two equal groups of 30 each. One group was treated with prophylactic intra-cameral dexamethasone at the end of phacoemulsification and the other group was given Balanced Salt Solution in its place. Both the groups were examined at post-operative day 1 and 7 for following parameters; best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), intra-ocular pressures (IOP), anterior chamber cells and flare.
Results: The dexamethasone group showed statistically significant improvement in anterior chamber cells and flare as compared to the placebo group at postoperative day 1 and 7 (p-value of 0.042 and 0.029 respectively for cells; p-value of 0.038 and 0.002 respectively for flare). HoweverBCVA and IOP showed no statistically significant differences between the two groups at postoperative day 1 and 7 (p-value 0.67 and 0.46 respectively for BCVA and 0.22 and 0.08 respectively for IOP).
Conclusion: Intra-cameral dexamethasone is an effective way to control postoperative inflammation following phacoemulsification with reduced anterior chamber cells and flare. However, its effects on BCVA and IOP were comparable to topical steroids.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 -

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






