Comparison of Intralesional Triamcinolone Acetonide Injection versus Surgical Intervention for Management of Primary Chalazion
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v38i4.1457
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v38i4.1457Abstract
Purpose: To compare the effectiveness of intralesional steroid injection versus Incision and curettage in management of primary chalazion.
Study Design: Quasi experimental study.
Place and Duration of Study: Department of Ophthalmology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad, from August 2020 to January 2021.
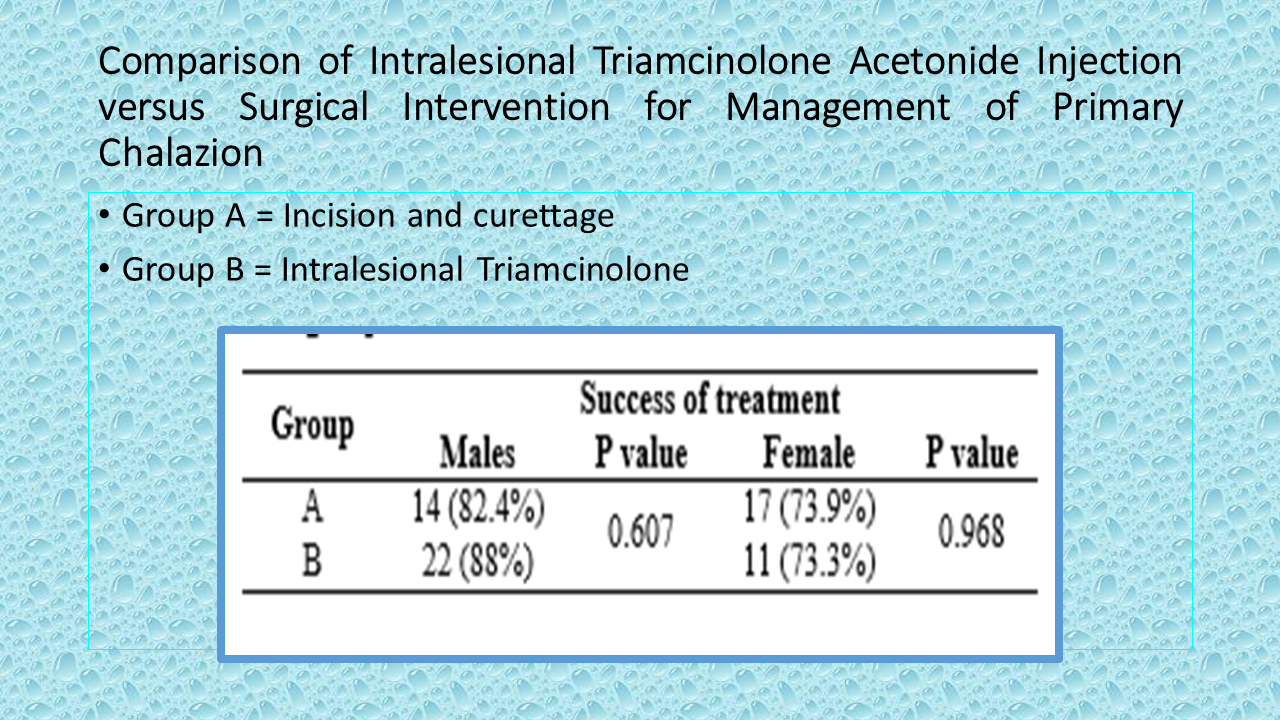
Methods: Eighty patients were divided into two groups of 40 each through consecutive sampling. Patients with primary chalazion of the size >5mm, age group 18 to 50 years and either gender were included. Patients with recurrent, multiple and infected chalazia were excluded. All patients underwent complete ocular examination. Group A underwent Incision and curettage while in group B a 28 gauge needle with a 1 ml syringe was used to inject 0.25 ml of 40 mg/ml Triamcinolone Acetonide into the chalazion via transcutaneous route. Success was defined as 80% reduction in the size of chalazion after one month. The chi-square test was used for equivalence of treatment efficacy between the groups.
Results: Age range in this study was 18 to 50 years. Mean age was 34.10 ± 5.87 years in Group A and 35.975 ± 7.60 years in Group B. The procedure was successful in 31 (77.5%) individuals in group A and 33 (82.5%) individuals in group B (P = 0.576), which was statistically insignificant. Stratification with respect to gender and age also showed no statistically significant difference between the two groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Intralesional steroid injection and Incision/curettageare equally effective in management of primary chalazion.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Hafiz Muhammad Jahanzaib, ijaz Khan, Fahmina Nazir, Amina Khalid, Nida Armoghan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






