Frequency of Post-Operative Hypotony with Sutureless Sclerotomy versus Intrascleral Hydration in 23-Gauge Pars-Plana Vitrectomy
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v38i4.1454
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v38i4.1454Abstract
Purpose: To compare the frequency of hypotony after 23-gauge (G) pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with suture-less sclerotomy versus intrascleral hydration for sclerotomy closure in eyes with air/gas tamponade.
Study Design: Quasi-experimental study.
Place and Duration of Study: College of Ophthalmology and Allied Vision Sciences, Mayo Hospital, Lahore from November 2021 to May 2022.
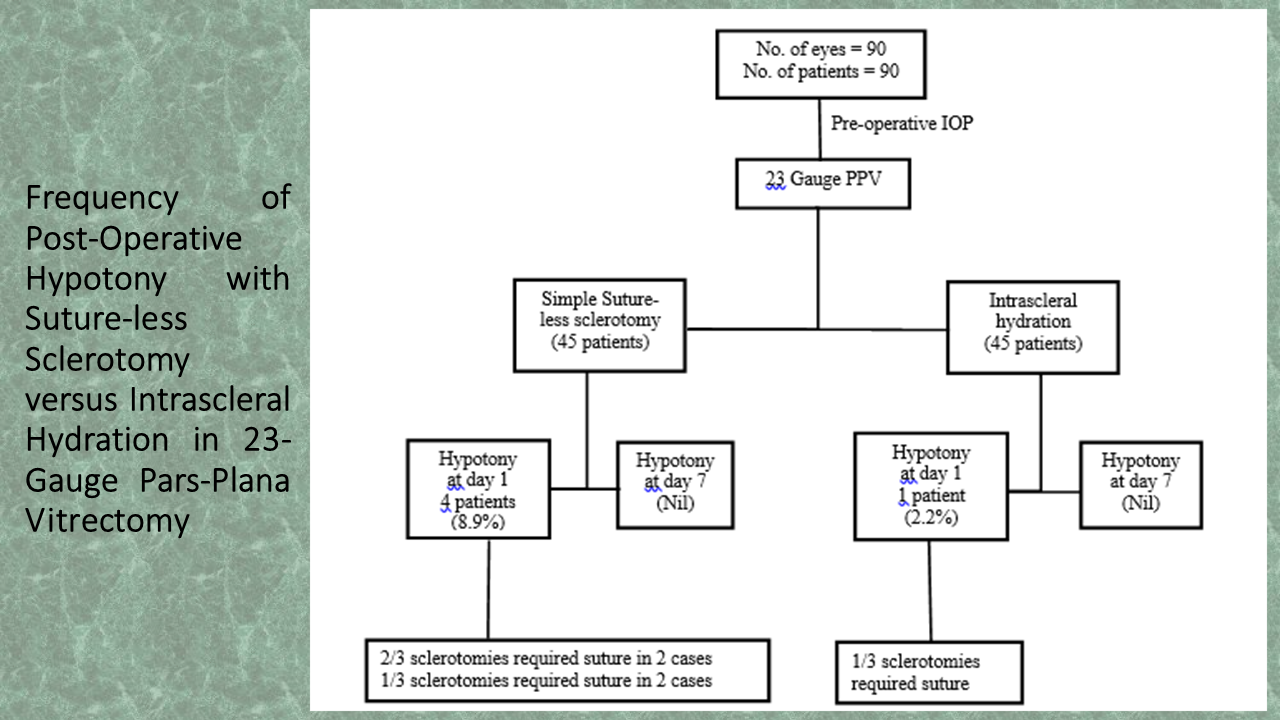
Methods: A total of 90 eyes were included who underwent PPV with air/gas tamponade. One group underwent PPV with suture-less sclerotomy while the other got intrascleral hydration for sclerotomy closure. Intraocular pressure (IOP) was measured pre and post-operatively at day one and day seven by applanation tonometry in all eyes. IOP of 6 mmHg or less was defined as hypotony. Primary endpoint measure was rate of early post-operative hypotony.
Results: A total of 90eyes of 90 patients, 40 (44.4%) males, and 50 (55.6%) females were included in the study. Five (5.6%) patients reported hypotony, out of which, only one (2.2%) case was seen in the intrascleral hydration group while rest (8.9%) were of the sutureless group. Sclerotomies requiring sutures were 4.44% (6 of 135) in sutureless group while 0.74% (1 of 135) in intrascleral hydration group. Paired sample T-test for the means of pre-operative and post-operative IOP was significantly different in both groups. For suture-less PPV, mean difference was 3.089 ± 7.960 mmHg (P = 0.013), while for the intra scleral hydration group, it was 3.778 ± 7.048 mmHg (p = 0.001).
Conclusion: Intrascleral hydration is a suitable option for PPV sclerotomy closure without having any side effects.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Amna Rizwan, Sidrah Latif, Asad Aslam Khan, Rana Muhammad Mohsin Javaid, Tehseen Majhu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






