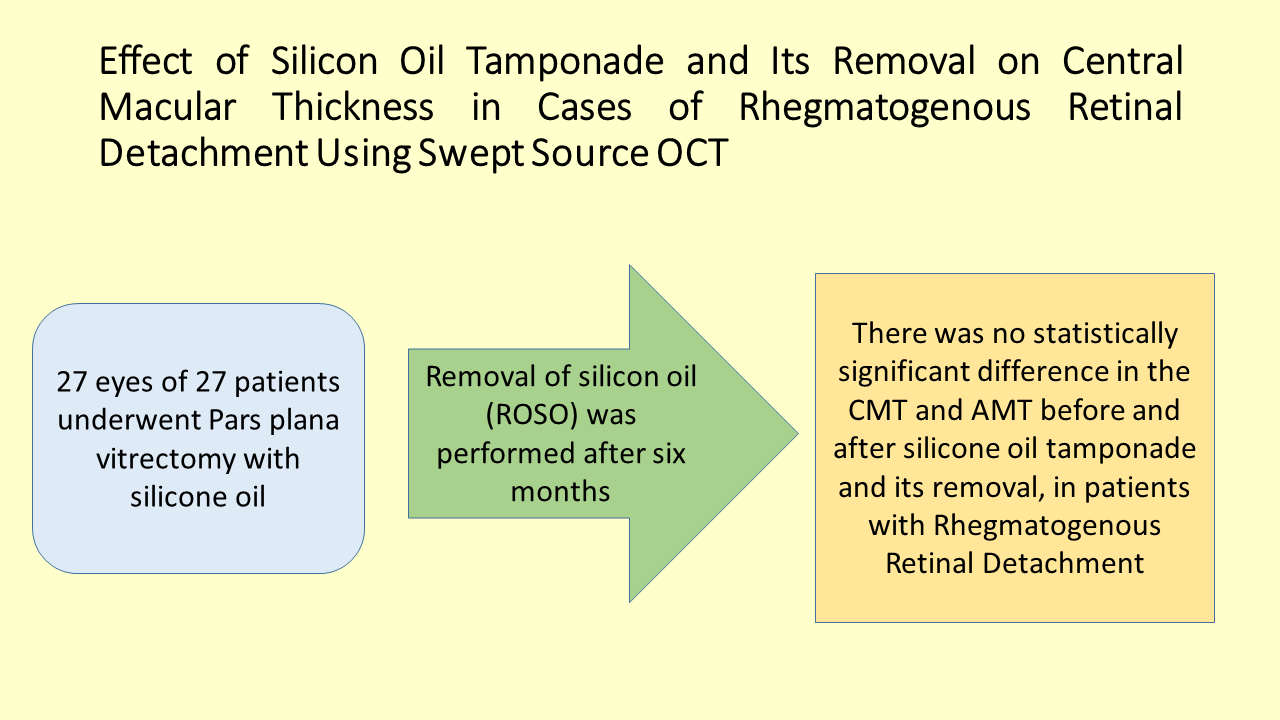
Effect of Silicon Oil Tamponade and Its Removal on Central Macular Thickness in Cases of Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Using Swept Source OCT
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v38i4.1437
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v38i4.1437Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effect of silicone oil (SO) tamponade and its removal on central macular thickness (CMT) and average macular thickness (AMT).
Study Design: Quasi experimental study.
Place & Duration of Study: Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi, from June 2021 to April 2022.
Methods: A total of 27 patients with 27 eyes with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment were included. Pars Plana Vitrectomy (PPV) with SO tamponade was performed. Removal of silicon oil (ROSO) was performedafter six months. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) was done before PPV, one month after PPV and one month after ROSO. The Central macular thickness (CMT) and Average macular thickness (AMT) were measured and compared between operated and control eyes.
Results: The mean CMT and AMT before surgery was 230 ± 60.5 μm and 253.3 ± 40.3 μm respectively. The mean CMT one month after PPV with SO was 281 ± 62.8 μm and 232 ± 62.2 μm in the operated eyes and control eyes (p = 0.053). Mean AMT one month after PPV with SO was 294 ± 98.7 μm and 253 ± 37.0 μm in operated and control eyes (p = 0.182). Mean CMT one month after SO removal was 222 ± 81.5 μm in operated eyes and 230 ± 59.2 μm in control eyes (p = 0.056). Mean AMT one month after SO removal was 263 ± 45.0 μm in operated eyes and 254 ± 21.4 μm in the control eyes (p = 0.087).
Conclusion: There was no statistically significant difference in the CMT and AMT before and after silicone oil tamponade and its removal, in patients with Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Muhammad Faisal Syed, Muhammad Ali Tahir, Najeeb Achakzai, Sabeen Abbasi, Azizur Rehman Arain

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






